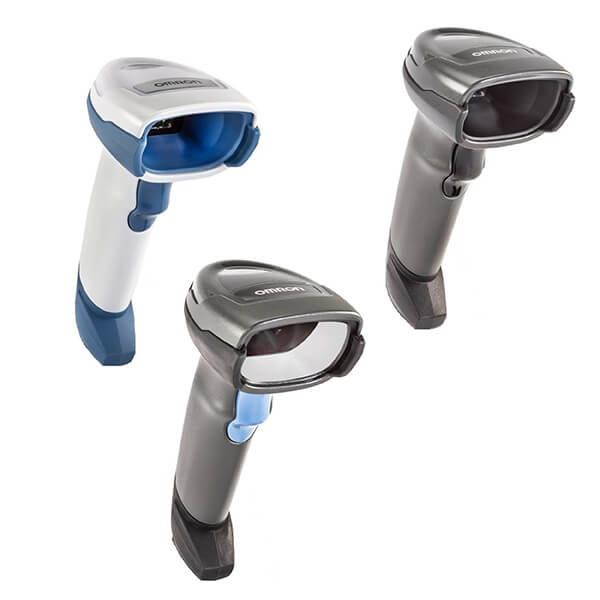
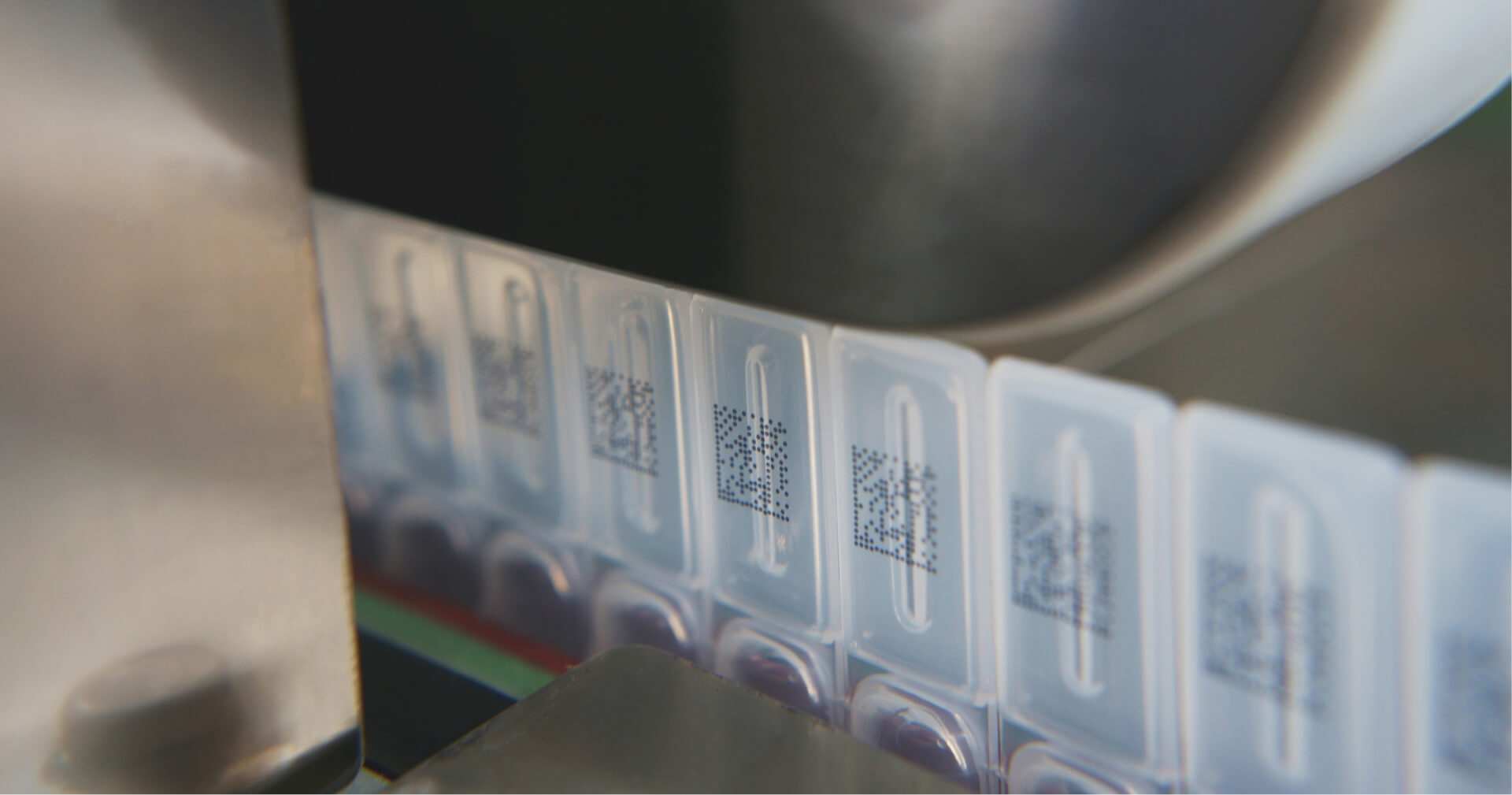
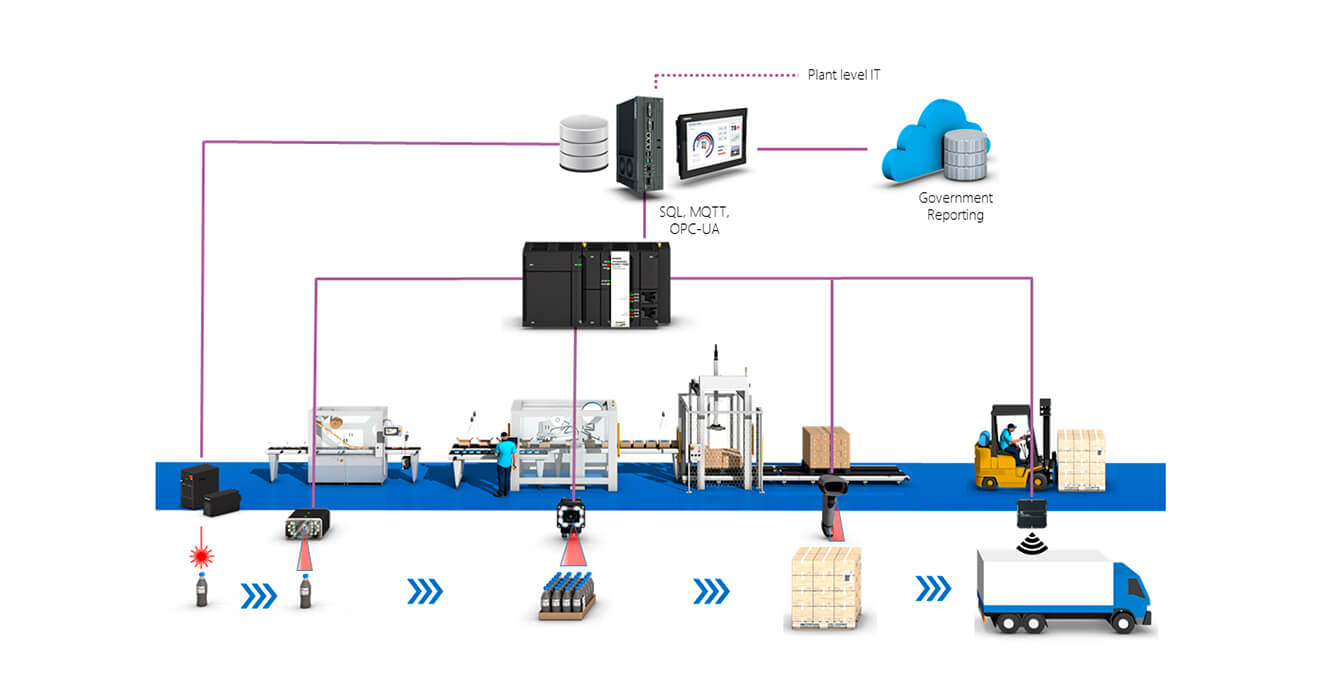
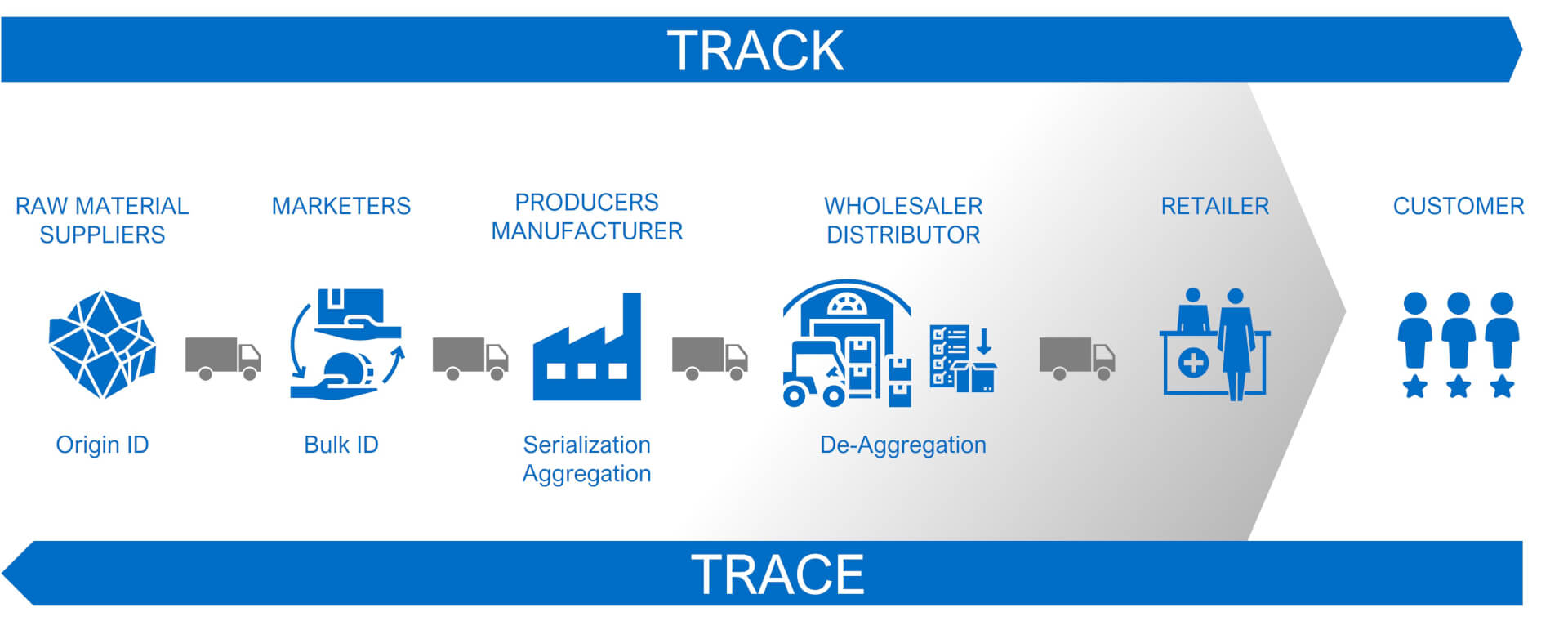
Traceability
This page aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of traceability in manufacturing, focusing on its fundamental principles and practical applications within the manufacturing industry.
- Code Reading and RFID: Discover how code reading and RFID technology enhance traceability through efficient data capture.
- Laser Marking: Learn how laser technology is used for permanent product marking ensuring reliable tracking and traceability for the lifetime of the product (cradle to grave).
- Communication: Explore the importance of real-time data exchange in traceability processes.
- Implementation: Gain insights into practical strategies for setting up robust traceability systems and ensuring data quality.
- Code inspection: Discover how code inspection or barcode verification technology plays a crucial role in maintaining traceability by ensuring the readability and accuracy of product codes and labels.
What is traceability?
What is Serialization?
Challenges
What is traceability in manufacturing?
What is lot traceability in manufacturing?
Do you want to know more about Traceability in Manufacturing?
Contact Our Experts Traceability in Manufacturing

Thank you for submitting your request. We will come back to you as soon as possible.
We are experiencing technical difficulties. Your form submission has not been successful. Please accept our apologies and try again later. Details: [details]
DownloadWhat is Track and Trace in Manufacturing?
So, what gets tracked?
How is it used in the industry?
In the manufacturing industry, the growing importance of traceability cannot be overstated. It's crucial to have real-time knowledge of the whereabouts of components or products within the production line, as well as throughout the supply chain.
Various technologies and tools are employed to implement track and trace systems. Some of the technologies include:
- Barcodes, QR codes, or RFID chips/tags
- Labelling systems, laser markers, barcode verification systems
- Real-Time Locating Systems (e.g., GPS)
- Code readers and scanners, tablets, or smartphones
- Software solutions
The trend finds applications across numerous areas, including:
- Tracking progress in manufacturing and production processes
- Ensuring the traceability of components
- Locating tools, machinery, testing, and measuring equipment
What is Code Reading and RIFD?
Barcode Types
Digimarc Barcodes: The Next Big Thing?
Our solutions for Traceability in manufacturing
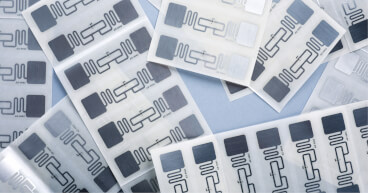
RFID Asset Tracking
*Unique RFID tags for precise asset identification. *RFID tags can store additional asset data. *Tags attached to assets, data captured wirelessly, and real-time updates.

Laser Marking
*Laser marking for durable, permanent, excellent quality codes. *Fiber laser markers with deep marking and 3D capabilities. *Benefits include marking on diverse materials and high-resolution markings.

Code Quality Verification
*Ensuring reliable traceability with 100% code readability. *Solutions for compliance with ISO and GS1 standards. *Benefits include documented compliance, guaranteed readability and reduced downtime.

Code Reading Challenges
*Overcoming challenges in reading codes in harsh environments. *Solutions with advanced decoding algorithms for reading even the poorest of quality codes. *Benefits include reading damaged codes and reliable reading in challenging conditions.

Communication & Implementation
*Efficient data collection in traceability. *Cost-effective implementation with database and communication enabled controllers. *Support for SQL, MQTT, REST and OPC-UA
What are the benefits of traceability in manufacturing?
Quality Control
Product Safety
Regulatory and Legal Compliance
Supply Chain Optimization
Brand Reputation
Types of Traceability in Manufacturing
Internal Traceability: Imagine you have a specific area, like a single company or a factory. Inside that area, you want to keep track of how parts or products move around. For instance, if a car engine assembly plant buys parts like camshafts and pistons from suppliers and puts them together, they use internal traceability to keep a record of these parts' history and quality checks.
Chain Traceability: Now, think bigger. Chain traceability covers the entire journey of a product, from getting the raw materials and parts to making, distributing, and selling it. Manufacturers can track where their products have gone ("trace forward"), and customers can find out where the products they have come from ("trace back"). This helps manufacturers investigate issues and recall products if needed. It also gives consumers confidence in the products they choose, knowing they can trust their origin.
Trace Forward and Trace Backward Traceability
Manufacturing traceability and Industry 4.0
Ensuring Compliance and Quality Control
Staying Compliant: Regulatory Compliance and Standards
Exploring the Link Between Traceability, Regulatory Standards and Compliance
The Role of Traceability in Meeting Industry-Specific Regulations
Global Standards for Traceability and Their Implications on Manufacturing
There are several international standards that relate to traceability in manufacturing, such as the ISO 9001 Quality Management System and ISO 14001 Environmental Management System. These global standards set forth the best practices for traceability that manufacturers across the world can implement to streamline operations, improve quality, and maintain compliance in the global market.
In conclusion, effective traceability in manufacturing is indispensable for staying compliant with regulatory compliance and standards. It is not just about fulfilling a requirement but plays a vital role in safeguarding the interest of stakeholders, including customers, regulators, and the manufacturers themselves.
GS1 Global Traceability Standard
Traceability PDF Whitepapers
Related Products
-

MicroHAWK F420-F Smart Camera
-

MicroHAWK F430-F Smart Camera
-

MicroHAWK F440-F Smart Camera
-

Faster machine operation, cameras for every application
-

High-speed, high-accuracy inspection and measurement
-

LVS-9510 Desktop Barcode Verifier
-

LVS-9580 Handheld Barcode Verifier
-

LVS-9585 Handheld DPM Barcode Verifier
-

MX-Z20XXH-V1 Fiber Laser Marker
-

MS-3 Compact Laser Barcode Scanner
-

QX-830 Industrial Barcode Scanner
-

QX-870 Industrial Raster Laser Scanner
-

Print Quality Inspection Systems
-

MicroHAWK V320-F Multicode Reader
-

MicroHAWK V330-F Multicode Reader
-

High Resolution Handheld Barcode Reader
-

MicroHAWK V420-F Autofocus Multicode Reader
-

V430-F Industrial Ethernet Barcode Reader
-

3 in 1 RFID system: Antenna, Amplifier & Controller in a single compact housing
-

UHF RFID System
Do you want to know more about Traceability in Manufacturing?
Contact Our Experts Traceability in Manufacturing

Thank you for submitting your request. We will come back to you as soon as possible.
We are experiencing technical difficulties. Your form submission has not been successful. Please accept our apologies and try again later. Details: [details]
Download